Windows Blog
Hardware Requirements for Windows 11? A Quick Compatibility Check
Windows 11 is Microsoft’s latest operating system, designed to deliver a sleek interface, advanced features, and improved performance. However, before diving into the upgrade, it’s crucial to ensure your hardware requirements. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essentials for checking compatibility and preparing your system for Windows 11.
Why Compatibility Matters
Windows 11 comes with stricter hardware requirements than its predecessors, focusing on security, efficiency, and modern computing capabilities. If your device doesn’t meet the minimum specifications, you may encounter performance issues or be unable to install the OS altogether.
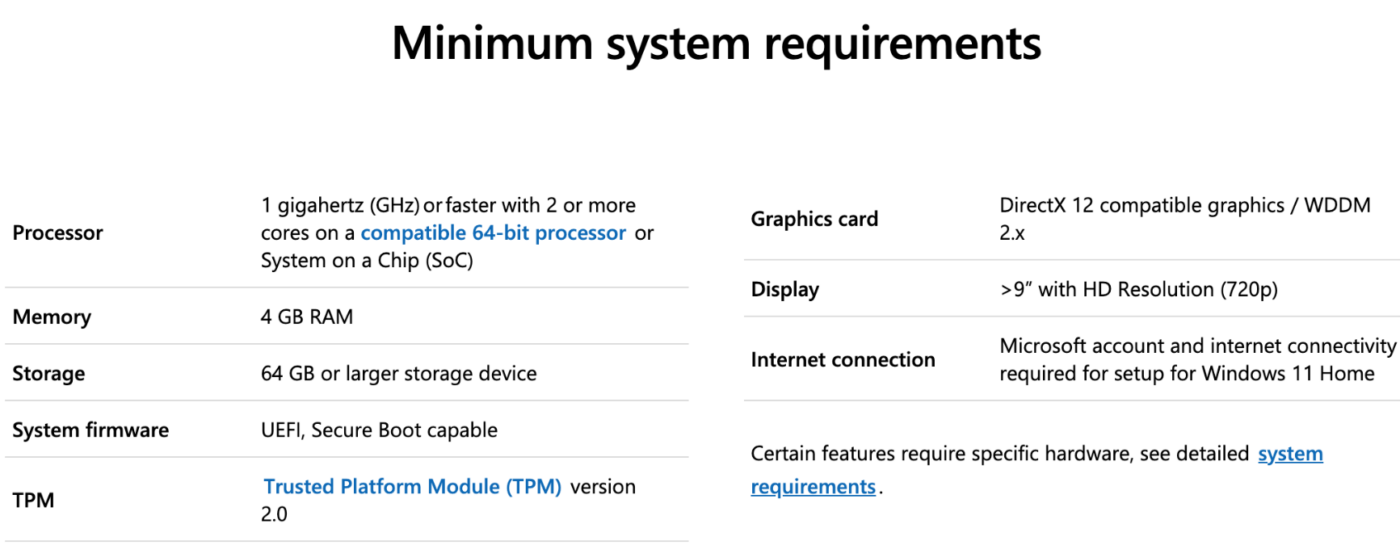
Minimum Hardware Requirements for Windows 11
To run Windows 11, your device must meet the following basic requirements:
- Processor: A compatible 64-bit processor with at least 1 GHz clock speed and 2 or more cores.
- RAM: Minimum 4 GB.
- Storage: At least 64 GB of available storage space.
- Graphics Card: DirectX 12-compatible graphics card or integrated GPU with a WDDM 2.0 driver.
- Display: A high-definition (720p) display, larger than 9 inches diagonally.
- Firmware: UEFI firmware with Secure Boot capability.
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0 enabled.
How to Check Your Hardware Compatibility
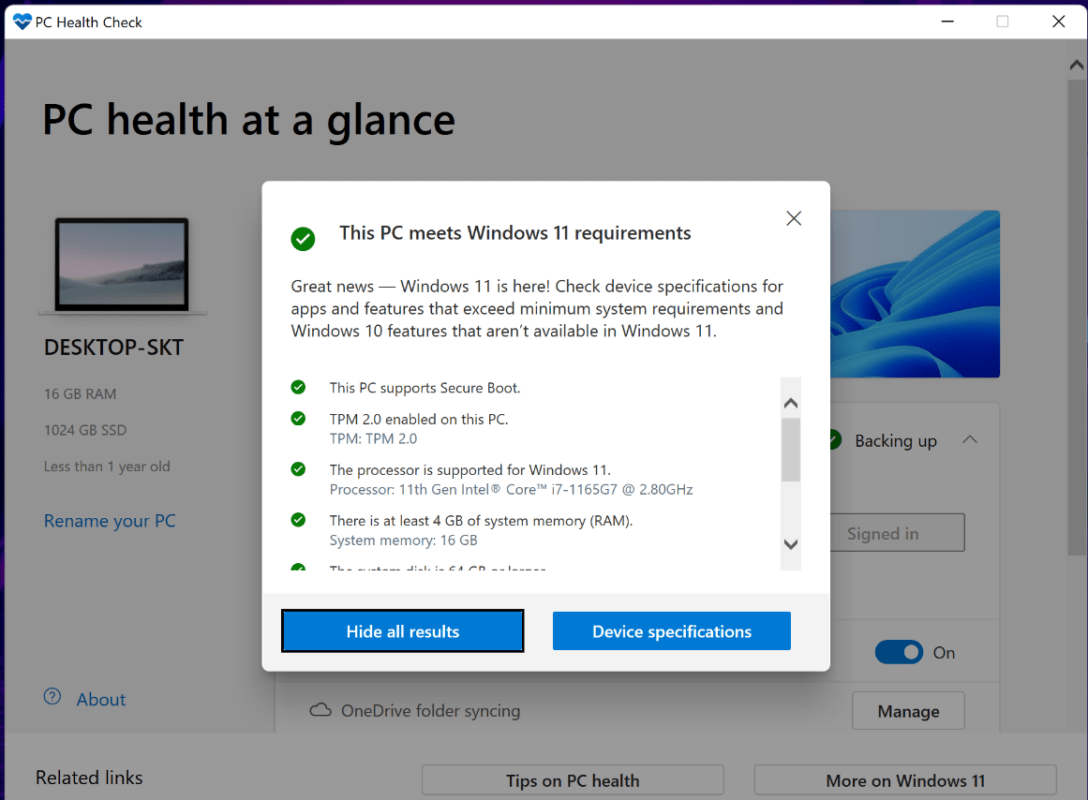
1. Use the PC Health Check Tool
Microsoft offers a free tool called PC Health Check that quickly determines if your hardware is ready for Windows 11. Follow these steps:
- Download the tool from the official Microsoft website.
- Run the application, and click “Check now” under the Windows 11 section.
- Review the results, which will highlight areas that meet or fail the requirements.
2. Check Manually
If you prefer to assess compatibility yourself, you can verify each requirement:
- Processor and RAM: Access the system information panel by typing
msinfo32in the Start menu search bar. - TPM 2.0: Open the Run dialog (
Win + R), typetpm.msc, and press Enter. This will confirm if TPM 2.0 is active on your device. - UEFI and Secure Boot: Access your BIOS/UEFI settings during startup (usually by pressing F2, F10, or DEL) and ensure Secure Boot is enabled.
What If Your PC Isn’t Compatible?
If your system doesn’t meet the requirements, don’t worry. Here are some potential solutions:
Upgrade Your Hardware
- Add More RAM: If your system falls short on memory, upgrading RAM is relatively straightforward and cost-effective.
- Replace Your Processor: This might require a motherboard upgrade as well, so check compatibility carefully.
- Enable TPM and Secure Boot: Many modern motherboards already support TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot. Visit your BIOS/UEFI settings to activate these features.
Get genuine Windows 11 keys at unbeatable prices—upgrade your PC affordably and securely today!

