Office Blog
Word’s Equation Editor: A Guide for Math & Science
Microsoft Word is more than just a tool for writing letters and reports. For those working in fields like mathematics, science, engineering, and finance, Word also provides powerful features to create complex equations and formulas. One of the most underutilized but essential tools in Word is the Equation Editor.
Whether you’re preparing a math assignment, science paper, or technical report, Word’s Equation Editor allows you to insert beautifully formatted, professional equations that will help your document look polished and make your content easier to understand.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about using Word’s Equation Editor to create precise, formatted equations and formulas in your documents.
What is Word’s Equation Editor?
Word’s Equation Editor is a built-in feature that allows you to insert mathematical equations and scientific formulas into your document. It’s designed to support a wide range of complex expressions—from simple arithmetic to advanced calculus and physics equations.
With this tool, you can type and format equations directly in your document without needing any external software or tools. It provides a user-friendly interface with a variety of options to create both basic and highly complex mathematical formulas.
Step 1: Accessing the Equation Editor
To access the Equation Editor in Microsoft Word, follow these simple steps:
- Place your cursor where you want the equation to appear in your document.
- Go to the Insert tab in the Word ribbon.
- Click on Equation (located in the Symbols group).
- A drop-down menu will appear with a selection of predefined equations and a button labeled Insert New Equation.
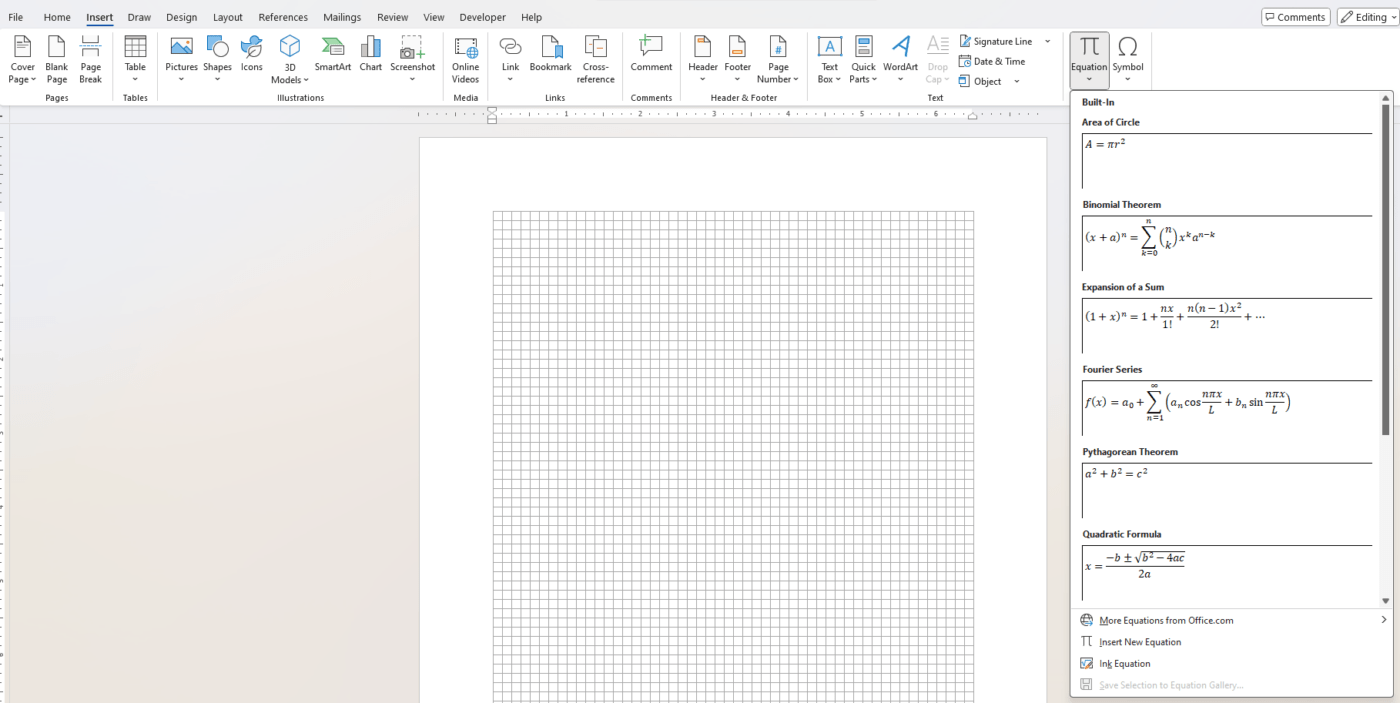
🔹 Pro Tip: You can also use the shortcut Alt + = to quickly open the Equation Editor!
Step 2: Using Predefined Equations
If you need a common mathematical or scientific equation, Word provides a number of predefined templates you can insert into your document.
How to Use Predefined Equations:
- Click Insert New Equation from the Equation drop-down.
- Choose one of the predefined equations listed in the menu, such as fractions, square roots, integrals, or summation formulas.
- Click on the equation, and Word will insert it into your document.
- You can then customize the equation by clicking inside it and editing the placeholders.
🔹 Pro Tip: Predefined equations are a great time-saver when you need to insert standard formulas like Pythagorean Theorem or quadratic equations.
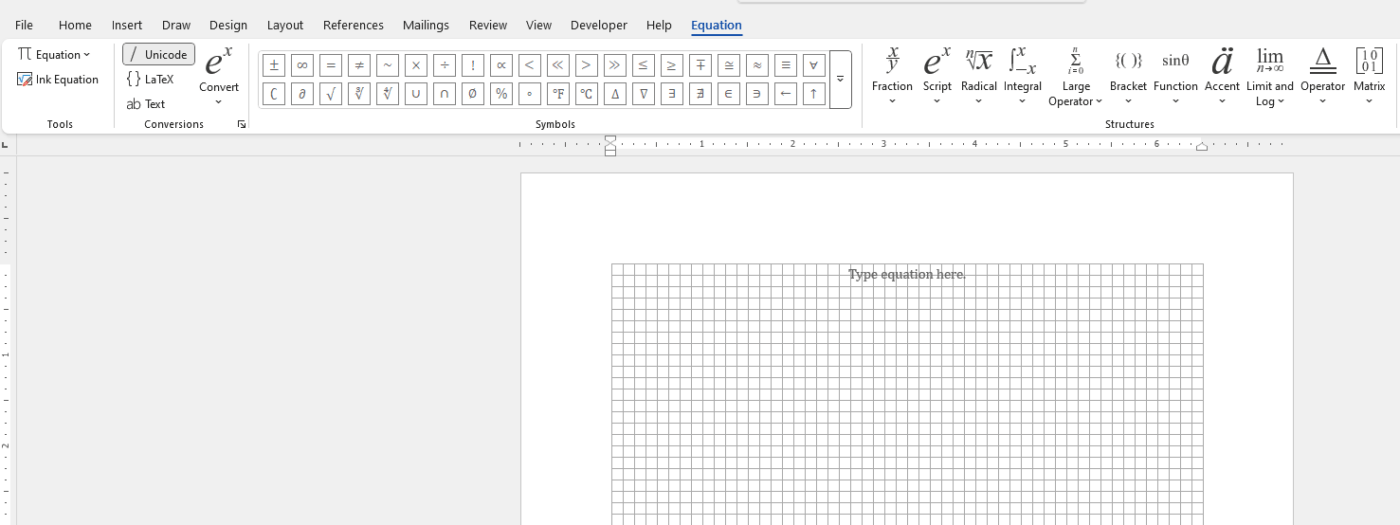
Step 3: Creating Custom Equations
While predefined equations are useful, you may need to create your own custom equation. This is where Word’s Equation Editor truly shines.
How to Create Custom Equations:
- Click on Insert New Equation to open the Equation Editor.
- You’ll see a toolbar at the top with a variety of mathematical symbols, structures, and functions, including:
- Fractions
- Exponents & Indices
- Radicals
- Operators (plus, minus, multiplication, etc.)
- Greek letters (used in scientific notation)
- Summation and integral symbols
- Use the toolbar to insert the necessary components of your equation. For example, click on the Fraction button to create a fraction or the Exponent button to add exponents.
Step 4: Formatting Your Equations
Word provides a variety of options to format and fine-tune your equations. You can control aspects like font size, style, alignment, and positioning.
How to Format Equations:
- Select the equation you’ve created.
- Use the Equation Tools that appear in the ribbon to customize the formatting. This includes options to:
- Resize your equation (in case it’s too large or too small).
- Change the font (if needed).
- Adjust the alignment of the equation (left, right, or centered).
Adding Superscripts and Subscripts:
If you need to add exponents or subscripts (like in chemical formulas), use the Exponent and Subscript buttons from the Equation Editor toolbar.
🔹 Pro Tip: Use the Equation Tools → Design tab for quick formatting and style options that make equations more visually appealing.
Step 5: Editing and Modifying Equations
After you’ve inserted an equation, you can go back and edit it at any time. Simply click on the equation to reactivate the Equation Editor, and then make your changes. You can:
- Modify the equation components (e.g., add terms, change operators).
- Resize or adjust the spacing between symbols.
- Replace symbols like π, ∞, or √ from the toolbar.
🔹 Pro Tip: Use the Right-click option to bring up additional editing options, such as Delete or Copy.
Step 6: Advanced Features for Math & Science
For those in specialized fields like engineering, physics, or chemistry, Word’s Equation Editor supports advanced functions such as:
- Matrices
- Vectors
- Differential equations
- Chemical reactions and stoichiometry
To access these advanced symbols and templates, use the Equation Tools → Design tab and select the appropriate options for your field.
🔹 Pro Tip: If you’re dealing with complex formulas, combine the Equation Editor with Word’s AutoCorrect feature to create custom shortcuts for commonly used equations (e.g., typing “\int” for an integral symbol).
Get the cheapest Office keys at unbeatable prices! Enjoy instant delivery and activate your Office suite hassle-free. Upgrade today and save big!

